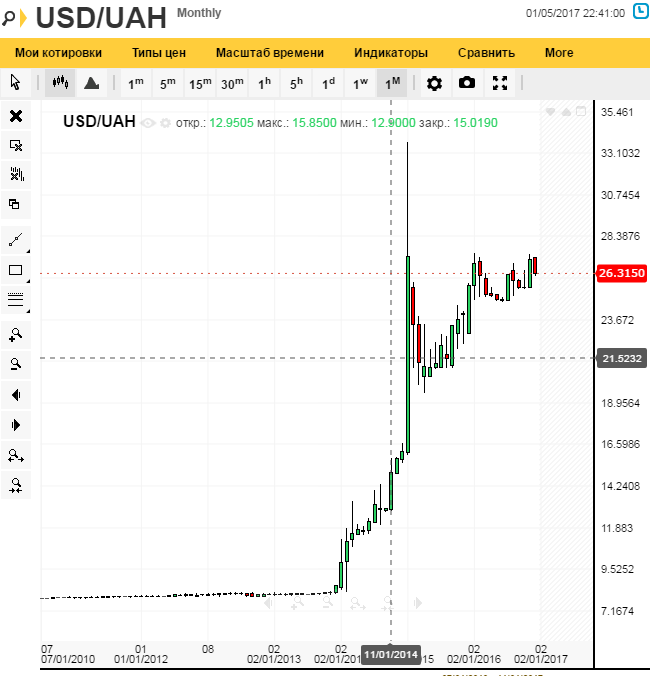
A “highly leveraged” company is one that has taken on significant debt to finance its operations. The firm has five percent bonds aggregating Rs. 4,00,000 and 10% shares amounting Rs. 2,00,000. Assuming the EBIT being 60,000 and Rs. 1,40,000, how would the EPS be affected. Given future uncertainty in the economy, the firm estimates that earnings before interest and taxes could vary anywhere from Rs.400,000 to Rs.2 million. So, financial leverage increased from 28% in 2016 to 33% in 2017 to 34% in 2018.
L. J. Gitman defines financial leverage as the firm’s ability to use fixed financial charges to magnify the effects of changes in EBIT on the firm’s earnings per shares. The degree of financial leverage indicates the financial risk involved in a firm. The knowledge of financial leverage helps in judiciously designing the capital structure of a firm in such a way to reduce the overall cost. The understanding of financial leverage also helps in the capital budgeting of a project. Financial leverage signifies the use of debt and preferential share capital for magnifying the profit available to the equity shareholders.

Classical Laminate Theory is chock full of matrices and I am not the guy (yet!) to go there with you. Fortunately there are lots of books, articles and real engineers to help you out. You have 600g of fiber in the +/-45-directions and 200g in the 0 and 90-directions. At 45 degree increments, the approximate fiber in each direction is enough to give a uniform “strength” in any direction.
Types of Leverages – Operating Leverage, Financial Leverage and Combined Leverage
Capital Structure cannot affect the total earnings of a firm but it can affect the share of earnings of equity shareholders. On the other hand variable cost are expenses that vary with organization’s production output and sales volume. Therefore, Operating leverage is a measure to establish relation between a firm’s fixed cost and variable cost and its impact of profits. Of making profits, these costs are of two types namely, fixed cost and variable costs. Fixed costs are expenses incurred in the course of business that does not change with an increase or decrease in the production and sales volume. The degree of financial leverage in a firm depends on its capital structure.
- A company will not have operating leverage if it does not have any fixed operating costs.
- Even there is a change in sales, the EPS will not get a huge impact due to a lower sensitivity.
- The degree of operating leverage is calculated by dividing a company’s EBIT by its revenue.
- Traditionally, the short-term finances are excluded from the methods of financing capital budgeting decisions, so, only long term sources are taken as a part of capital structure.
- However, it can also cause a manifold decline in EPS when EBIT declines.
A prime number has two factors, a composite number has more than two.
Formula for Calculating Combined Leverage
At an output level of 110,000 units, firm A has a profit of Rs.80,000, while firm B has a profit of Rs.105,000. Increased leverage will magnify profits at high levels of output but will magnify losses at low levels of production. Once a higher level of fixed costs is assumed, it is difficult to eliminate these costs if sales do not reach the expected level.
In this ratio, operating leases are capitalized and equity includes both common and preferred shares. Instead of using long-term debt, an analyst may decide to use total debt to measure the debt used in a firm’s capital structure. The formula, in this case, would include minority interest and preferred shares in the denominator. Combined leverage explains the combined effect of operating leverage and financial leverage of a firm on its earnings per share . Thus, it explains the changes in EPS on account of changes in sales.
Accountancy and Financial Management – Notes | Study Accountancy and Financial Management – B Com
So it can be concluded that a firm should always have a high financial leverage corresponding to a low operating leverage. If this is taken into consideration none of the said three firms have faithfully followed the norms. The degree of combined leverage may be calculated by multiplying the degree of operating leverage and the degree of financial leverage. If the firm earns a return on investment less than the rate at which it pays interest to debt holders, then it negative or unfavourable leverage. In such a situation, firm pays the interest on debt from the profit belonging to the shareholders. The surplus after payment of fixed financial charges belong to equity owners.
The degree of operating leverage may be defined as the change in the percentage of operating income , for a given change in percentage of sales revenue. The degree of operating leverage at any level of output is arrived at by dividing the percentage change in EBIT with percentage change in sales. Operating Risk or Business Risk is the risk of not being able to meet fixed operating costs. The higher the fixed operating costs, the higher will be operating leverage and the higher will be operating risk of the business. The coefficient of variation of the expected earnings from total assets, defined business risk. A high financial leverage indicates that the firm increase its ROE after applying debt-financing in its capital structure.
The ratio helps a company discern its best possible levels of operational and financial leverage. Thus Financial Leverage indicates the dependency of business on debt financing over equity finance for its financial decision making. The use of Long Term Fixed Interest Bearing Debt and Preference Share Capital along with Equity Share Capital is called as Financial Leverage.
However, most analysts consider that UPS earns enough cash to cover its debts. A leverage ratio is any one of several financial measurements that look at how much capital comes in the form of debt or assesses the ability of a company to meet its financial obligations. A firm with high operating leverage may sell its products at reduced prices because of presence of lower variable cost per unit.
Leverage Ratio: What It Is, What It Tells You, How To Calculate
Therefore, a company should always try to avoid having higher operating leverage if it is not sure about the stability of its sales. If the sales are fluctuating and highly vulnerable then a high DOL condition is a highly risky proposition. Fixed operating costs are those operating costs which are independent of output. These costs remain constant irrespective of the production and sales data. An example of combined leverage would be if a company’s sales increased by 10%, while the eps increased by 16.67%.
Financial risk is the analying of company EPS change due to change in operating income. Leverage results from using borrowed capital as a source of funding when investing to expand a firm’s asset base and generate returns on risk capital. Total-debt-to-total-assets is a leverage ratio that shows the total amount of debt a company has relative to its assets. Exploration costs are typically found in the financial statements as exploration, abandonment, and dry hole costs. Other noncash expenses that should be added back in are impairments, accretion of asset retirement obligations, and deferred taxes.
Financial leverage pinpoints the correct profitable financial decision regarding capital structure of the company. Financial leverage measures the percentage of change in taxable income to the percentage change in EBIT. Operating leverage assists to identify the position of fixed cost and variable cost. Operating leverage is one of the procedures to measure the impact of changes in sales which lead for change in the profits of the company. If there is any change in the sales, it will lead to corresponding changes in profit.
When they evaluate whether they can increase production profitably, they address operating leverage. If they are expecting taking on additional debt, they have entered the field of financial leverage. Operating leverage and financial leverage both heighten the changes that occur to earnings due to fixed costs in a company’s capital structures. Fundamentally, leverage refers to debt or to the borrowing of funds to finance the purchase of a company’s assets. Business proprietors can use either debt or equity to finance or buy the company’s assets. Use of debt, or leverage, increases the company’s risk of bankruptcy.
Examples of Financial Leverage Formula (With Excel Template)
Any units which are produced beyond 25,000 units yields operating profits. Therefore, any increases in sales, fixed costs remaining same, increases operating profit. The increase in percentage operating income due to percentage, composite leverage formula of increase in sales is called as “Degree of operating leverage”. Operating leverage shows the ability of a firm to use fixed operating cost to increase the effect of change in sales on its operating profits.
Practically the range is about 0.2 to 0.7 – which is still quite a range. The equity multiplier is a calculation of how much of a company’s assets is financed by stock rather than debt. A high debt/equity ratio generally indicates that a company has been aggressive in financing its growth with debt. This can result in volatile earnings as a result of the additional interest expense.
With the preferred stock issue, the impact on earnings per share is more volatile because the preferred dividends are paid on an after-tax basis. Thus the earnings per share will vary from a deficit of Rs.3.84 to Rs.12.80. Financial leverage is defined as the extent to which the firm utilizes limited participating funds obtained at a fixed cost in the hopes of increasing returns to common shareholders. Financial leverage may be favorable when the company earns more on the assets purchased with the funds, then the fixed cost of their use. And financial leverage may be unfavorable when the company does not earn as much as the funds cost.
High leverage indicates high financial risks which would signal the finance manager to select the securities carefully. The two quantifiable tools, viz., operating and financial leverage are adopted to know the earnings per share and also which shows the market value of the share. Thus, financial leverage is a better tool compared to operating leverage. Change in EPS due to changes in EBIT results in variation in market price.
